Audio Sample Rate
Samples are taken at a regular time intervals called the sampling rate. The sampling rate is responsible for the frequency response of the digitized sound.
According to the Nyquist theorem (named after Harry Nyquist), the highest reproducible frequency of a digital system is 1/2 the sampling rate, often called the Nyquist frequency.
A sampling rate of 44,100 samples per second, the rate at which CD's are encoded, can reproduce frequencies up to 22,050 Hz, well above the 20,000 Hz limit of human hearing. Frequencies that are recorded above the Nyquist frequency may foldover at a much lower frequency than the original, which is called aliasing.
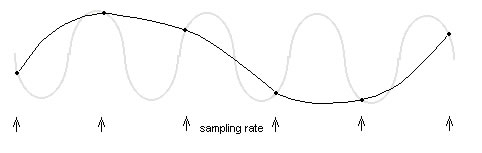
On this picture aliasing produces waveform at 1/4 the original signal's frequency.
Therefore, steep (brickwall) filters are usually put in front of an ADC input to prevent signals above the Nyquist frequency from ever entering the system. In direct synthesis, where waveforms are produced 'synthetically' by a computer program, it is desirable to use 'band-limited' waveforms whose frequency components do not exceed the Nyquist frequency.
Standard sampling rates are 44.1K are 48K (and even 96K in some high-end recording systems). See the result of two different sample rates below.
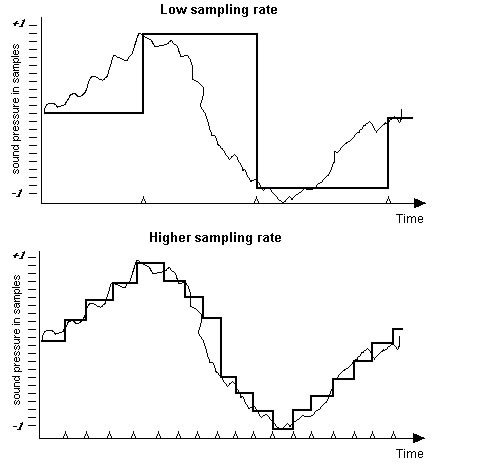
|
|
Music Editing Master is an ideal and efficient audio editing software for home users. It provides powerful and user-friendly editing environment which suits beginners especially

|
|
|